Crowdfunding tutorial
This repository contains tutorials for the Crowdfunding Application! Here you will find how to create and deploy your Smart Contract using the Klever IDE.
Pre Requisites
- Install VSCode and the Rust Analyzer extension.
- Install the Klever IDE Plugin.
- Clone this repository and install the dependencies using cargo.
git clone https://github.com/klever-io/kvm-contract-example
Creating the Contract
The full code of the Crowdfunding contract is available here.
-
Open the cloned project in VSCode. You should see this following folder structure:
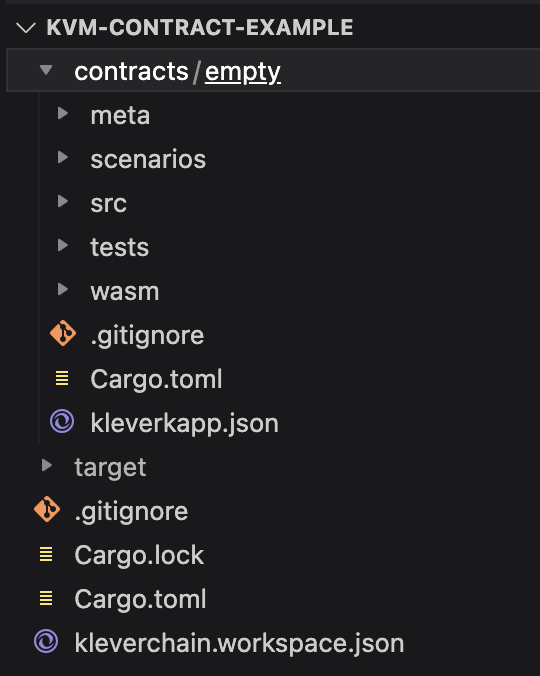
-
Let's start editing the
Cargo.tomlfile from the root. Change the path of thecontracts/emptytocontracts/crowdfunding.
members = ["contracts/crowdfunding", "contracts/crowdfunding/meta"]
- Let's rename the empty folder to
crowdfunding. And inside theCargo.tomlfile, change the path of theemptytocrowdfunding. And thesrc/empty.rstosrc/lib.rs.
[package]
name = "crowdfunding"
[lib]
path = "src/lib.rs"
- Now let's do the same thing for the
metaandwasmfolder.
# Wasm
[package]
name = "crowdfunding-wasm"
[dependencies.crowdfunding]
path = ".."
# Meta
[package]
name = "crowdfunding-meta"
[dependencies.crowdfunding]
path = ".."
-
Now let's start with the
crowdfundingcontract. Open thesrc/lib.rsfile that must contain the following code: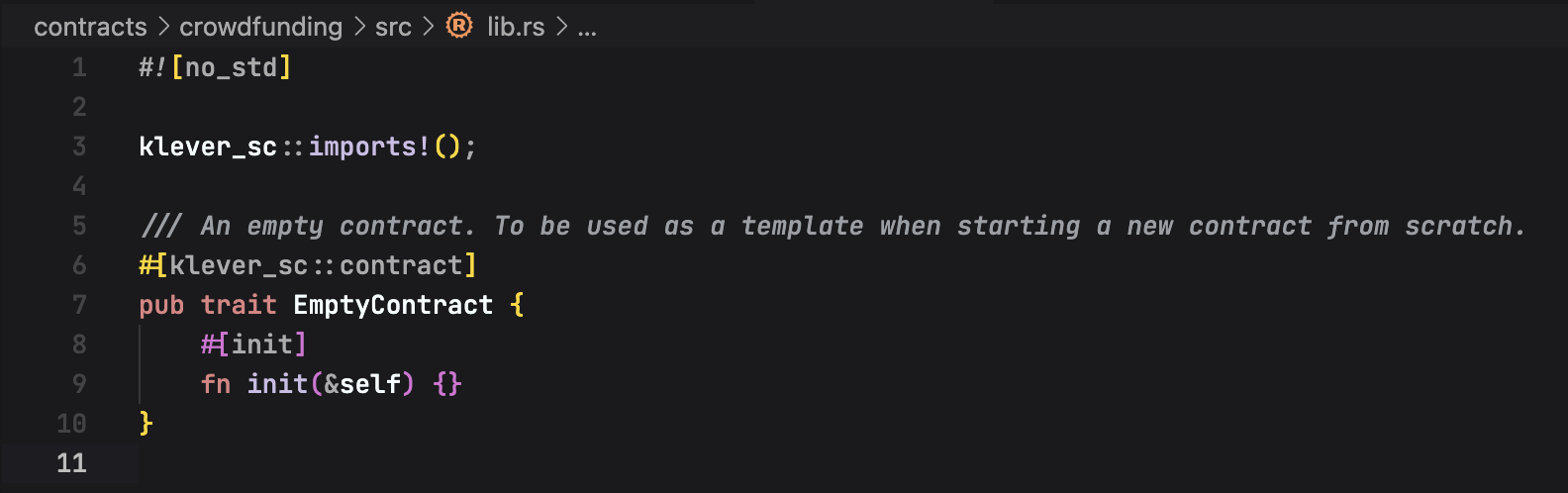
-
First, let's create a file to contain the Crowdfunding struct. Inside the
crowdfundingfolder, create a file calledcrowdfunding_data.rsand add the following code:
use klever_sc::{
api::ManagedTypeApi,
types::{BigUint, ManagedAddress, ManagedBuffer, TokenIdentifier},
};
klever_sc::derive_imports!();
#[derive(NestedEncode, NestedDecode, TopEncode, TopDecode, TypeAbi, ManagedVecItem)]
pub struct CrowdfundingData<M: ManagedTypeApi> {
pub id: ManagedBuffer<M>,
pub title: ManagedBuffer<M>,
pub logo: ManagedBuffer<M>,
pub description: ManagedBuffer<M>,
pub owner: ManagedAddress<M>,
pub token: TokenIdentifier<M>,
pub balance: BigUint<M>,
pub claimed: BigUint<M>,
pub target: BigUint<M>,
pub donators: u64,
pub deadline: u64,
}
This struct will contain all the data that we need to store for the Crowdfunding contract. And show to the final user. You can check all types that is being used here.
- Now let's think on all the data that must be stored in the blockchain, to fill all frontend features and contract functionalities. We will need to store the following data:
- Profit Address: The address that will receive the profit from every Crowdfunding Claim.
- Service Fee: The percentage that the platform will receive from every Crowdfunding Claim.
- Claim Fee: The fixed fee value that the platform will receive from every Crowdfunding Claim.
- Crowdfundings: A list of all Crowdfundings based by an Unique ID (Key)
- Crowdfunding by Owner: A list of all Crowdfundings IDs based by owner address (Key)
- Crowdfunding Holders: A list of all Unique Crowdfundings Holders
- Crowdfunding Limit: The maximum amount stored in the Last Crowdfundings
- Last Crowdfundings: The last Crowdfundings ID that was created.
- Let's create a file called
storage.rsinside thecrowdfundingfolder and add the following code:
klever_sc::imports!();
klever_sc::derive_imports!();
use crate::crowdfunding_data::CrowdfundingData;
#[klever_sc::module]
pub trait Storage {
#[storage_mapper("profitAddress")]
fn profit_address(&self) -> SingleValueMapper<ManagedAddress>;
#[view(getServiceFee)]
#[storage_mapper("fee")]
fn service_fee(&self) -> SingleValueMapper<u32>;
#[view(getLimit)]
#[storage_mapper("limit")]
fn limit(&self) -> SingleValueMapper<u32>;
#[view(getClaimFee)]
#[storage_mapper("claimFee")]
fn claim_fee(&self) -> SingleValueMapper<BigUint>;
#[view(getCrowdfunding)]
#[storage_mapper("crowdfunding")]
fn crowdfunding(
&self,
id: &ManagedBuffer,
) -> SingleValueMapper<CrowdfundingData<Self::Api>>;
#[storage_mapper("crowdfundingHoldersValues")]
fn crowdfundings_holders_values(&self, address: &ManagedAddress) -> VecMapper<ManagedBuffer>;
#[storage_mapper("crowdfundingsHolders")]
fn crowdfundings_holders(&self) -> VecMapper<ManagedAddress>;
#[storage_mapper("lastCrowdfundings")]
fn crowdfundings(&self) -> VecMapper<ManagedBuffer>;
}
Note: The views of VecMapper will be created in the next steps.
-
Take a look in the macros that we are using in the code above. We are using the
#[storage_mapper]to store the data in the blockchain. The#[view]to create a function that will be exposed in the Node API. -
Now let's create the Storage Setters that only the contract owner can call. Create a file called
storage_setters.rsinside thecrowdfundingfolder and add the following code:
klever_sc::imports!();
klever_sc::derive_imports!();
use crate::storage;
#[klever_sc::module]
pub trait StorageSetters: storage::Storage {
#[only_owner]
#[endpoint]
fn set_profit_address(&self, address: ManagedAddress) {
self.profit_address().set(address);
}
#[only_owner]
#[endpoint]
fn set_fee(&self, fee: u32) {
self.service_fee().set(fee);
}
#[only_owner]
#[endpoint]
fn set_limit(&self, limit: u32) {
self.limit().set(limit);
}
#[only_owner]
#[endpoint]
fn set_claim_fee(&self, fee: BigUint) {
self.claim_fee().set(fee);
}
}
-
Take a look in the
#[only_owner]macro that we are using in the code above. This macro will check if the caller is the contract owner. And also in the trait inheritance: storage::Storage. -
Now let's create more view functions to get expose more specifically data that we need to show in the frontend. Create a file called
crowdfunding_views.rsinside thecrowdfundingfolder and add the following code:
- The
getLastCrowdfundingsfunction will return the last Crowdfundings that was created. We only store the ID, so we need to iterate over the IDs and get each Crowdfunding data. - The
getCrowdfundingsByHolderfunction will return all Crowdfundings by a holder. So we need to get all IDs and then iterate over the IDs and get each Crowdfunding data. - The
getCrowdfundingHoldersfunction will return all Crowdfundings Holders. So we need to iterate over the addresses and return them.
klever_sc::imports!();
klever_sc::derive_imports!();
use crate::{storage, crowdfunding_data::CrowdfundingData};
#[klever_sc::module]
pub trait CrowdfundingViews: storage::Storage {
#[view(getLastCrowdfundings)]
fn get_last_crowdfundings(&self) -> ManagedVec<CrowdfundingData<Self::Api>> {
let mut vec = ManagedVec::new();
let ids = self.crowdfundings();
for id in &ids {
let crowdfunding = self.crowdfunding(&id).get();
vec.push(crowdfunding);
}
vec
}
#[view(getCrowdfundingHolders)]
fn get_crowdfunding_holders(&self) -> ManagedVec<ManagedAddress> {
let mut vec = ManagedVec::new();
let holders = self.crowdfundings_holders();
for holder in &holders {
vec.push(holder.clone());
}
vec
}
#[view(getCrowdfundingsByHolder)]
fn get_crowdfundings_by_holder(&self, address: &ManagedAddress) -> ManagedVec<CrowdfundingData<Self::Api>>{
let mut vec = ManagedVec::new();
let ids = self.crowdfundings_holders_values(address);
for id in &ids {
let crowdfunding = self.crowdfunding(&id).get();
vec.push(crowdfunding);
}
vec
}
}
-
Take a look in the
#[view]macro that we are using in the code above. And also in the trait inheritance: storage::Storage. -
Now are only missing the Crowdfunding functionalities. Create a file called
crowdfunding_methods.rsinside thecrowdfundingfolder and add the following code:
klever_sc::imports!();
klever_sc::derive_imports!();
use crate::storage;
use crate::crowdfunding_data::CrowdfundingData;
use crate::crowdfunding_helpers::{name_to_id, discount_percentage_fee};
#[klever_sc::module]
pub trait CrowdfundingMethods: storage::Storage
{
// Awesome code
}
- But before start coding the Crowdfunding functionalities, let's create a file called
crowdfunding_helpers.rsinside thecrowdfundingfolder and add the following code:
- The
name_to_idfunction will receive the Crowdfunding Name as a buffer and return a new buffer with the name in lowercase and without spaces. Here we are managing directly with bytes, so we need to use thefor_each_batchfunction to iterate over the bytes and apply the logic. - The
discount_percentage_feefunction will receive the amount and the percentage and return the amount minus the percentage fee. Here we are using theBigUinttype to handle the amount and thediv,mulandsubfunctions to apply the logic.
use core::ops::Div;
use core::ops::Mul;
use core::ops::Sub;
use klever_sc::{
api::ManagedTypeApi, types::{ManagedBuffer, BigUint}
};
pub fn name_to_id<M: ManagedTypeApi>(buffer: &ManagedBuffer<M>) -> ManagedBuffer<M> {
let mut ret = ManagedBuffer::new();
buffer.for_each_batch::<1, _>(|batch| {
let byte_to_append = match batch[0] {
b' ' => b'-',
b'A'..=b'Z' => batch[0] + (b'a' - b'A'),
b'0'..=b'9' | b'a'..=b'z' | b'-' => batch[0],
_ => return,
};
ret.append_bytes(&[byte_to_append]);
});
ret
}
pub fn discount_percentage_fee<M: ManagedTypeApi>(amount: &BigUint<M>, percentage: u32) -> BigUint<M> {
let fee = amount.clone().div(&BigUint::from(100u32));
let final_fee = fee.clone().mul(&BigUint::from(percentage));
let claim_value = amount.clone().sub(final_fee.clone());
claim_value
}
- Now come back to the Crowdfunding functionalities. Open the
crowdfunding_methods.rs.
Create Code
- The
createfunction will receive all the data that we need to create a new Crowdfunding. We will check if the name is valid, if the deadline is valid, if the target is valid and if the Crowdfunding already exists. Then we will create a new Crowdfunding and store the data in the blockchain. If the limit is reached, we will remove the first Crowdfunding and add the new one.- The
require!macro is used to add validations to the code. - The
#[endpoint]macro is used to expose the function in Contract Invoke. - The
name_to_idfunction is used to convert the name to an ID. - The
self.blockchain().get_caller()function is used to get the caller address. - The
self.blockchain().get_block_timestamp()function is used to get the current block timestamp.
- The
#[endpoint]
fn create(&self, name: ManagedBuffer, logo: ManagedBuffer, description: ManagedBuffer,
token: TokenIdentifier, target: BigUint, deadline: u64) {
let id = name_to_id(&name);
require!(id.len() > 3, "Invalid name!");
require!(deadline > self.blockchain().get_block_timestamp(), "Invalid deadline!");
require!(target > BigUint::default(), "Invalid target!");
require!(self.crowdfunding(&id).is_empty(), "Crowdfunding already exists!");
let caller = &self.blockchain().get_caller();
let crowdfunding = CrowdfundingData{
id: id.clone(),
title: name.clone(),
logo: logo.clone(),
description: description.clone(),
token: token.clone(),
owner: caller.clone(),
balance: BigUint::default(),
claimed: BigUint::default(),
target: target.clone(),
donators: 0,
deadline,
};
self.crowdfunding(&id).set(crowdfunding);
if self.crowdfundings_holders_values(caller).is_empty() {
self.crowdfundings_holders().push(caller);
}
self.crowdfundings_holders_values(caller).push(&id);
let limit = self.limit().get() as usize;
if self.crowdfundings().len() < limit {
self.crowdfundings().push(&id);
return;
}
for (i, _) in self.crowdfundings().iter().enumerate() {
if i == 0 {
continue;
}
self.crowdfundings().set(i, &self.crowdfundings().get(i+1))
}
self.crowdfundings().set(limit, &id);
}
Donate Code
- The
donatefunction will receive the Crowdfunding ID and the payment. We will check if the Crowdfunding exists, if the token is valid and if the token is the same as the Crowdfunding. Then we will add the payment to the Crowdfunding balance and increment the donators.- The
require!macro is used to add validations to the code. - The
#[payable("*")]macro is used to receive any token as payment (CallValue). - The
#[endpoint] macrois used to expose the function in Contract Invoke. - The
self.call_value().klv_or_single_fungible_kda()function is used to get a single payment and the token identifier.
- The
#[endpoint]
#[payable("*")]
fn donate(&self, crowdfunding_id: ManagedBuffer) {
let (token_identifier, payment, _) = self.call_value().klv_or_single_fungible_kda();
require!(!self.crowdfunding(&crowdfunding_id).is_empty(),"Crowdfunding not found!");
let mapper = self.crowdfunding(&crowdfunding_id);
let mut crowdfunding = mapper.get();
require!(
token_identifier == crowdfunding.token,
"Invalid token for Crowdfunding!"
);
crowdfunding.balance += payment;
crowdfunding.donators += 1;
mapper.set(crowdfunding);
}
Set Deadline
- The
set_deadlinefunction will receive the Crowdfunding ID and the new deadline. And here we only need to check is the deadline provided is bigger than the current timestamp.- The
require!macro is used to add validations to the code. - The
#[endpoint]macro is used to expose the function in Contract Invoke. - The
self.blockchain().get_block_timestamp()function is used to get the current block timestamp.
- The
#[endpoint]
fn set_deadline(&self, crowdfunding_id: ManagedBuffer, deadline: u64) {
let mapper = self.crowdfunding(&crowdfunding_id);
let mut crowdfunding = mapper.get();
require!(!mapper.is_empty(),"Crowdfunding does not exists!");
require!(crowdfunding.owner == self.blockchain().get_caller(), "You are not the owner!");
let timestamp = self.blockchain().get_block_timestamp();
require!(deadline > timestamp, "Deadline already passed!");
crowdfunding.deadline = deadline;
mapper.set(crowdfunding);
}
Claim Code
- The
claimfunction will receive the Crowdfunding ID and the amount to claim. We will check if the Crowdfunding exists, if the deadline is passed, if the amount is valid and if the amount is less than the balance. Then we will calculate the profit and the claim value and transfer the claim value to the caller.- The
require!macro is used to add validations to the code. - The
#[endpoint]macro is used to expose the function in Contract Invoke. - The
#[payable("KLV")]macro is used to receive Only KLV as payment (CallValue). - The
self.blockchain().get_caller()function is used to get the caller address. - The
discount_percentage_feefunction is used to calculate the claim value. - The
self.send().direct_kdafunction is used to transfer the claim value to the crowdfunding owner.
- The
#[payable("KLV")]
#[endpoint]
fn claim(&self, id: ManagedBuffer) {
let (token_identifier, payment, _) = self.call_value().klv_or_single_fungible_kda();
require!(token_identifier == TokenIdentifier::from("KLV"), "Invalid token for claim!");
require!(payment == self.claim_fee().get(), "Invalid Fee for claim!");
require!(!self.crowdfunding(&id).is_empty(),"Crowdfunding does not exists!");
let mapper = self.crowdfunding(&id);
let mut crowdfunding = mapper.get();
require!(crowdfunding.owner == self.blockchain().get_caller(), "You are not the owner!");
let available = crowdfunding.balance.clone().sub(crowdfunding.claimed.clone());
require!(available > BigUint::from(0u32), "Claim not available!");
let fee = self.service_fee().get();
let claim_value = discount_percentage_fee(&available, fee);
self.send().direct_kda(&crowdfunding.owner, &crowdfunding.token, 0, &claim_value);
crowdfunding.claimed += &available;
let profit = available.clone().sub(&claim_value);
self.send().direct_kda(&self.profit_address().get(), &crowdfunding.token, 0, &profit);
crowdfunding.claimed += &available;
mapper.set(crowdfunding);
}
- Now let's create the Crowdfunding contract. Open the
src/lib.rsfile and add the following code:
#![no_std]
klever_sc::imports!();
klever_sc::derive_imports!();
mod storage;
mod storage_setters;
mod crowdfunding_data;
mod crowdfunding_views;
mod crowdfunding_methods;
pub mod crowdfunding_helpers;
#[klever_sc::contract]
pub trait Crowdfunding:
crowdfunding_methods::CrowdfundingMethods
+ storage_setters::StorageSetters
+ crowdfunding_views::CrowdfundingViews
+ storage::Storage
{
#[init]
fn init(&self, service_fee: u32, limit: u32, profit_address: ManagedAddress, claim_fee: BigUint) {
self.service_fee().set(service_fee);
self.profit_address().set(profit_address);
self.claim_fee().set(claim_fee);
self.limit().set(limit);
}
}
- The
#[init]macro is used to expose the function in Contract Deploy. - The
self.service_fee().set(service_fee)function is used to set the initial value of service fee. - The
self.profit_address().set(profit_address)function is used to set the initial value of profit address. - The
self.claim_fee().set(claim_fee)function is used to set the initial value of claim fee. - The
self.limit().set(limit)function is used to set the initial value of limit. - Take a look in the trait inheritance
: crowdfunding_methods::CrowdfundingMethods + storage_setters::StorageSetters + crowdfunding_views::CrowdfundingViews + storage::Storage.
- Now let's create the Crowdfunding Meta. Open the
src/lib.rsfile and add the following code:
fn main() {
klever_sc_meta::cli_main::<crowdfunding::AbiProvider>();
}
Deploying the Contract
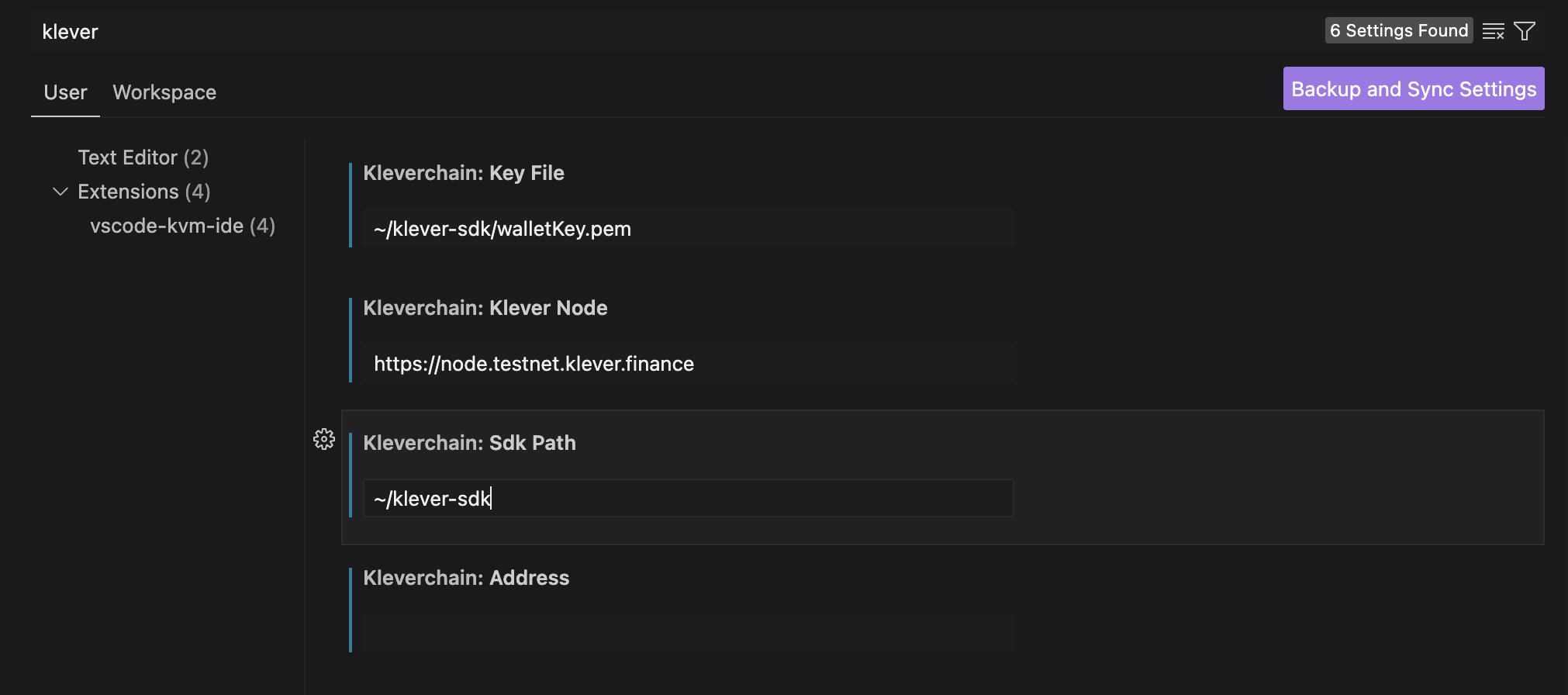
-
Open the VSCode Settings and search for Klever
-
Now let's fill the required field:
- Key File: The path to your .pem file that will be used to deploy the contract.
- Address: The address (refered to .pem) that will be used to deploy the contract.
- Node: You can use https://node.testnet.klever.org (Testnet) or https://node.mainnet.klever.org (Mainnet).
-
To create your own .pem file, you can access the KApps and click on the "Generate New Account" button.

-
Now you can Drag you .pem file to VSCode and open it.
-
Now you can fill the required fields.
-
If you are using the Tesnet you can ask for some Test KLV. Just run the following command on your terminal Make sure to replace with your address:
curl -X POST https://api.testnet.klever.org/v1.0/transaction/send-user-funds/klv1sr70jktl8rhq37s8htl390qm6mnx4wsdm5e8nykk797d6d3n85vsghyqd4
-
Now you can click on the Klever IDE Icon and Select the Crowdfunding, and with the rigth click, selec the option Build Contract.
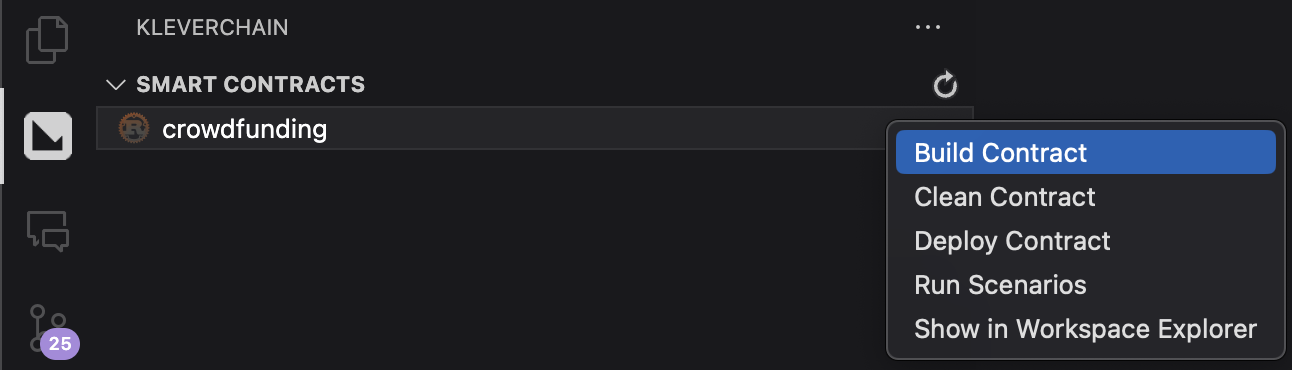
-
The output must be this:
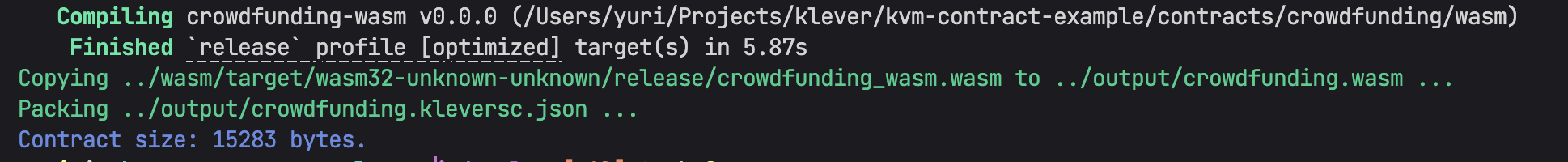
-
Now you can click on the Klever IDE Icon and Select the Crowdfunding again, rigth click, and select the option Deploy Contract.
-
The output will be an error, so you need to add in the end of the command the following arguments:
--args u32:5 --args u32:10 --args a:klv1sr70jktl8rhq37s8htl390qm6mnx4wsdm5e8nykk797d6d3n85vsghyqd4 --args bi:10000000
You can change the values of the service fee, limit, profit address and claim fee with precision.
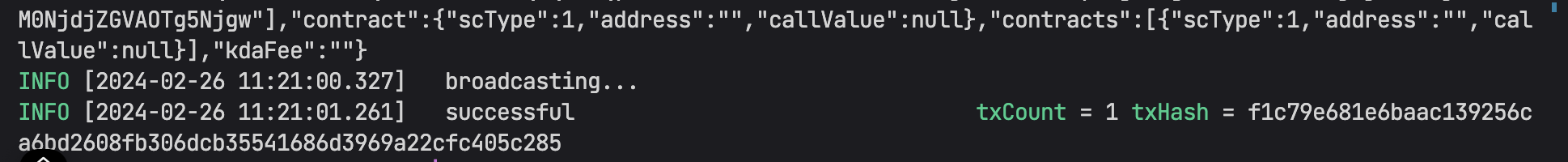
- If everything is ok, the output must copy the transaction hash and you can open in the Kleverscan to copy the contract address:
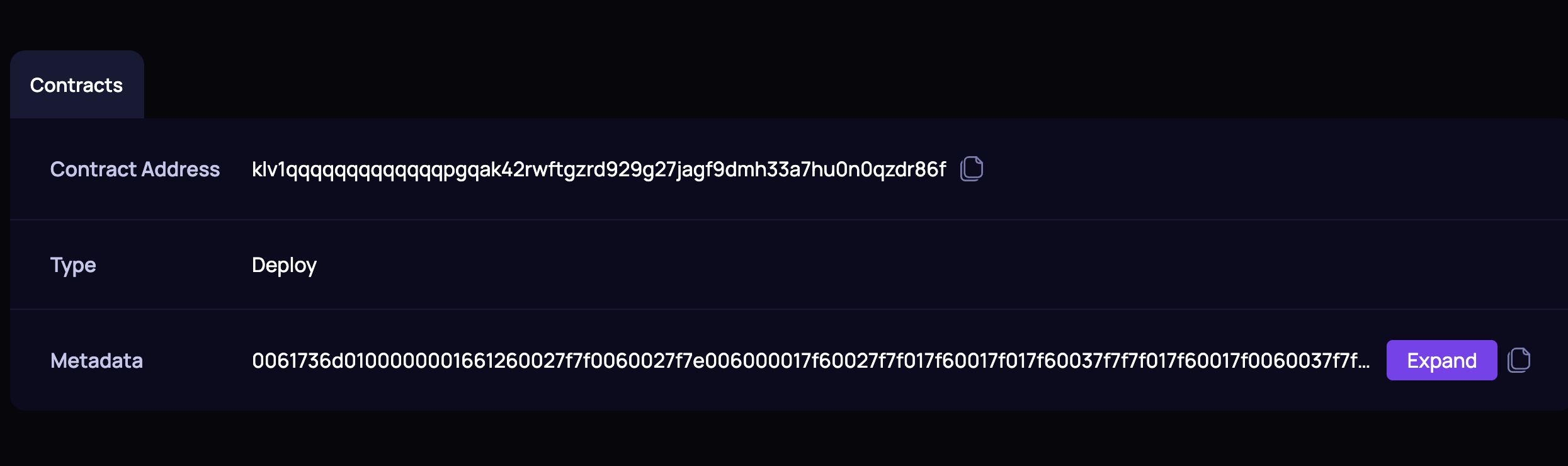
The crowdfunding.abi.json file is the
contracts/crowdfunding/outputfolder. This ABI file you will use in the frontend integration.
Frontend Integration
The full code of the Crowdfunding frontend is available here. Here we will show some examples of how to integrate the Crowdfunding contract with the frontend.
Pre Requisites
- Install the Klever SDK
- Create a ABI const in your code. Like This.
- Create the CrowdfundingData interface. Like This.
Get Last Crowdfundings
// setup constants
const nodeUrl = 'https://node.testnet.klever.org'
const scAddress = 'klv1qqqqqqqqqqqqqpgqak42rwftgzrd929g27jagf9dmh33a7hu0n0qzdr86f'
// fetch the last crowdfunding view
const req = await fetch(`${nodeUrl}/vm/hex`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
scAddress: scAddress,
funcName: 'getLastCrowdfundings',
args: [],
}),
})
// parse the response to JSON
const res = await req.json()
if (res.error !== '' || res.data.data === '') {
console.log('some error happened')
}
// parse the response to the CrowdfundingData interface
const decodedCrowdfundings = abiDecoder.decodeList(
res.data.data,
'List<CrowdfundingData>' // The type of the response (contains inside the ABI file),
abi // (The ABI const that you created),
)
console.log(decodedCrowdfundings)
Enconding the Create Function
const convertedValues = []
const deadlineConverted = new Date(deadline).getTime()
convertedValues.push(abiEncoder.encodeABIValue(title, 'String', false))
convertedValues.push(abiEncoder.encodeABIValue(image, 'String', false))
convertedValues.push(
abiEncoder.encodeABIValue(description, 'String', false),
)
convertedValues.push(abiEncoder.encodeABIValue(token, 'String', false))
convertedValues.push(abiEncoder.encodeBigNumber(target, false))
convertedValues.push(
abiEncoder.encodeABIValue(deadlineConverted, 'u64', false),
)
const metadata = convertedValues.join('@') // Note all values are separated by '@'
// create the transaction payload
const payload: ISmartContract = {
address: scAddress,
scType: 0,
}
// encode the metadata to base64, and add the 'create' prefix (function Name)
const txData: string = Buffer.from(
'create' + '@' + metadata,
'utf8',
).toString('base64')
try {
// build the transaction and validate the data
const unsignedTx = await web.buildTransaction(
[
{
payload,
type: TransactionType.SmartContract,
},
],
[txData],
)
// sign the transaction
const signedTx = await web.signTransaction(unsignedTx)
// broadcast the transaction
const broadcastResponse = await web.broadcastTransactions([signedTx])
// check if the transaction was broadcasted
if (
broadcastResponse.error !== '' ||
broadcastResponse.data.txsHashes.length === 0
) {
throw new Error('Error creating crowdfunding')
}
}
Enconding the Donate Function
const payload: ISmartContract = {
address: scAddress as string,
scType: 0,
callValue: {
[token.assetId]: amountParsed // The amount to donate, parsed to the token precision.
},
}
// encode the metadata to base64, and add the 'donate' prefix (function Name)
const txData: string = Buffer.from(
'donate' + '@' + abiEncoder.encodeABIValue(crowdfunding.id, 'String', false),
'utf8',
).toString('base64')
- Note that the
callValueis used to send the payment to the contract. And thetxDatais used to encode the function name and the arguments. - You need to use the abiEncoder to encode the values to the correct format.
- You need to use the abiDecoder to decode the values to the correct format from node hex value.
Conclusion
Now you can create and deploy your own Crowdfunding contract and integrate it with the frontend. You can use the Klever SDK to interact with the contract and the Klever Node to get the contract data. If you have any questions, feel free to ask in the Klever Forum.